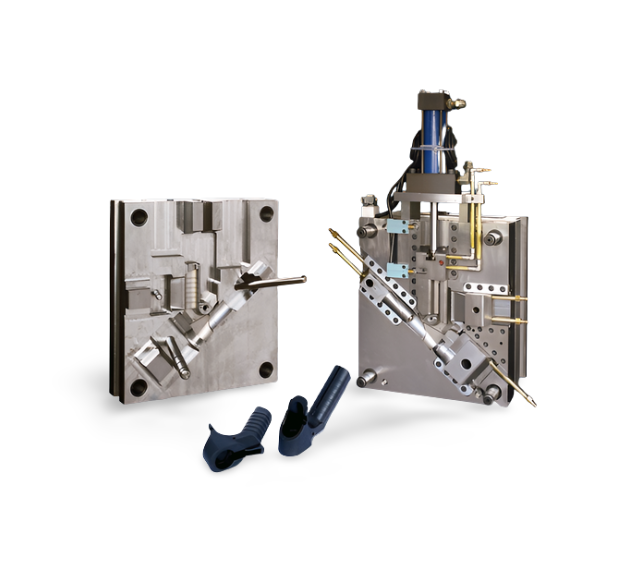
Molds, various molds and tools used in industrial production to obtain the desired product by injection, blow molding, extrusion, die-casting or forging, casting, stamping, etc. In short, a mold is a tool used to produce a molded article, a tool composed of several parts, different molds are made up of different parts. It is mainly used to process the shape of the article by changing the physical state of the material being molded.
So how is the mold made?
The following is a brief introduction to the modern mold production process.
1、ESI (EarlierSupplierInvolvement supplier early involvement): This stage is mainly a technical discussion between customers and suppliers about product design and mold development, etc. The main purpose is to let suppliers clearly understand the product designer’s design intention and precision requirements, and also let product designers better understand the mold production The main purpose is to let the supplier clearly understand the product designer’s design intention and precision requirements, and also to let the product designer better understand the ability of mold production and product process performance, so as to make more reasonable design.
2、Quotation:Including the price of the mold, the life of the mold, the turnover process, the number of tons required by the machine and the delivery time of the mold. (A more detailed quotation should include information such as product size and weight, mold size and weight, etc.)
3、Order(PurchaseOrder):Customer order, deposit issued and supplier order accepted.
4、ProductionPlanningandScheduleArrangement:This stage needs to respond to the customer for the specific date of delivery of the mold.
5、Mold Design:Pro/Engineer, UG, Solidworks, AutoCAD, CATIA, etc. are the possible design software.
6、Procurement of materials
7, mold processing (Machining): the processes involved are roughly turning, gong (milling), heat treatment, grinding, computer gong (CNC), electric discharge (EDM), wire cutting (WEDM), coordinate grinding (JIGGRINGING), laser engraving, polishing, etc.
8、Mold assembly (Assembly)
9、Mold trial (TrialRun)
10、Sample evaluation report (SER)
11、Sample evaluation report approval (SERApproval)
Mold making
The requirements for mould design and production are: accurate dimensions, neat surfaces, reasonable structure, high production efficiency, easy automation, easy manufacture, high life expectancy, low cost, design to meet the needs of the process and economic reasonableness.
The design of the mould structure and the selection of parameters should take into account factors such as stiffness, guidance, unloading mechanism, installation method and clearance size. The worn parts of the mould should be easy to replace. For plastic moulds and casting moulds, consideration should also be given to a reasonable pouring system, the flow of molten plastic or metal, the position and direction of entry into the cavity. In order to increase productivity and reduce pouring losses in the runners, multi-cavity moulds can be used, where several identical or different products can be completed simultaneously in a single mould. In mass production, high performance, high precision and long life moulds should be used.
Progressive multi-station moulds should be used for stamping, and progressive carbide block moulds can be used to increase service life. In small batch production and trial production of new products, moulds with simple structure, fast manufacturing speed and low cost should be used, such as combination punching moulds, thin plate punching moulds, polyurethane rubber moulds, low melting point alloy moulds, zinc alloy moulds and super plasticity alloy moulds. Moulds have begun to use computer-aided design (CAD), i.e. through a computer-centred set of systems to optimise the design of moulds. This is the development direction of mould design.
According to the structural characteristics, the mould making is divided into flat punching and cutting moulds and cavity moulds with space. Punching and cutting dies use precise dimensional adjustment of the convex and concave dies, some even with gapless adjustment. Other forging dies, such as cold extrusion dies, casting dies, powder metallurgy dies, plastic dies and rubber dies are cavity dies, which are used to form three-dimensional parts. Cavity moulds have dimensional requirements in 3 directions: length, width and height, and are complex in shape and difficult to manufacture. Moulds are generally produced in small batches and in single parts. The manufacturing requirements are strict and precise and use precision measuring machines and equipment.
Flat dies can initially be formed by electro-etching and then further increased in accuracy by contour and co-ordinate grinding. Shape grinding can be carried out with optical projection curve grinding machines or surface grinding machines with reduction and restoration wheel grinding mechanisms, or with special shape grinding tools on precision surface grinding machines. Coordinate grinding machines can be used for the precise positioning of moulds to ensure accurate bore and opening distances. Computer numerically controlled (CNC) continuous orbital co-ordinate grinding machines can also be used to grind any curved and hollow moulds. Hollow cavity moulds are mainly machined by contour milling, EDM and electrolytic machining. The combined use of contour profiling and CNC technology, as well as the addition of a three-directional flat head to EDM, can improve cavity quality. The addition of blowing electrolysis to electrolytic machining can increase productivity.
Post time: Jul-15-2022